NGINX is recommended by many experts when users need to find a powerful web server that can handle many simultaneous connections.
1. What is NGINX?
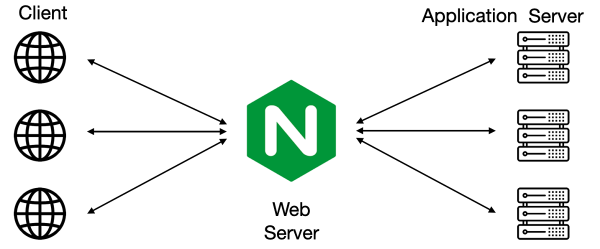
NGINX is a powerful open source web server. NGINX uses a single-threaded, event-driven architecture, making it more efficient than the Apache server. It can also do other important things, such as load balancing, HTTP caching, or use as a reverse proxy. NGINX is indispensable knowledge for a web developer, system administrator or developers.
2. NGINX’s operating principle
NGINX does not rely on threads for query processing. Instead, it will operate under an asynchronous event architecture. That is, similar threads will be managed in one process. Each of these processes contains smaller units called worker connections, which are responsible for processing the threads that provide workflow requests and sending them to the main process. Then, the master process will take on the task of returning results for those requests.
Each worker connection can handle up to 1024 similar requests. From there, it helps handle thousands of different requests without any problems. Therefore, NGINX is chosen by many people for websites with many requirements such as e-commerce sites, search engines, and clod storage.
3. What are advantages and disadvantages of NGINX
Advantages of NGINX
NGINX has gained widespread popularity and is increasingly being adopted due to its numerous strengths, including:
Enhanced Application Performance: NGINX’s robust caching mechanism efficiently handles repeat requests to the same address, significantly improving application performance.
Lightweight Web Server: NGINX operates as a lightweight web server, forwarding user requests to the application server seamlessly.
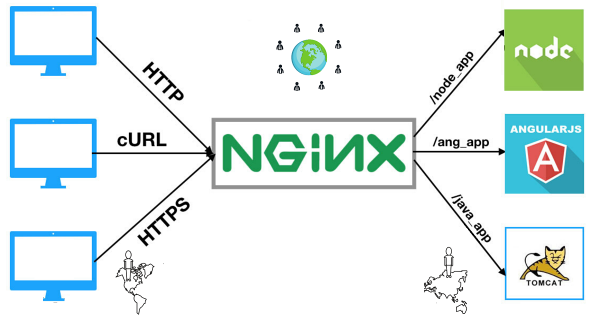
Flexible URL Rewriting: NGINX’s powerful rewrite rules provide exceptional flexibility for configuring permanent or temporary redirects for specific URLs.
HTTPS Compatibility: NGINX is easily customized and can be securely delivered over the HTTPS protocol, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
Scalable and Efficient: NGINX effectively handles up to 10,000 concurrent connections with a minimal memory footprint, making it highly scalable and resource-efficient.
Static File Serving and Indexing: NGINX excels at serving static files and creating appropriate file indexes, streamlining content delivery.
Simplified Load Balancing: NGINX’s ability to accelerate reverse proxies with caches simplifies load balancing, offering exceptional fault tolerance.
FastCGI, uWSGI, SCGI, and Memcached Support: NGINX seamlessly integrates with FastCGI, uwsgi, SCGI, and memcached servers, enabling efficient application acceleration.
Modular Architecture for Enhanced Performance: NGINX;smodular architecture empowers you to boost page loading speed through automatic gzip compression.
SSL/TLS Encryption for Secure Communication: Nginx inherently supports SSL and TLS encryption, safeguarding data exchanges against unauthorized access.
Flexible Configuration and Logging: NGINX’s highly flexible configuration simplifies saving query logs, providing valuable insights into application behavior.
Error Handling and URL Management: NGINX effectively redirects 3XX-5XX errors and rewrites URLs using expressions, ensuring seamless user experiences.
Rate Limiting and Connection Control: NGINX’s rate limiting capabilities prevent resource overload and safeguard against malicious attacks. It also allows you to control the number of concurrent connections and queries from specific IP addresses.
Embedded PERL Code Support: NGINX seamlessly integrates with PERL code, enabling customized functionality.
IPv6 Compatibility: NGINX fully supports IPv6, ensuring compatibility with the latest internet infrastructure.
Websocket Support: NGINX supports websockets, enabling real-time communication between web servers and clients.
Disadvantages of NGINX
- Load balancing is limited compared to other servers.
- The mechanism for storing and providing orders needs to be improved.
- Navigating between the Nginx homepage and customer support is difficult.
4. NGINX Main Feature
Load Balancing
Load balancing involves the strategic distribution of incoming traffic across multiple servers to enhance efficiency, improve reliability, and optimize response times for websites or applications. It is primarily employed when a single server becomes overwhelmed by the volume of requests. By deploying multiple servers, load balancers distribute workloads efficiently, preventing any one server from becoming overloaded and ensuring the best utilization of each server’s capacity.
Reverse Proxy
The deployment of a reverse proxy offers significant advantages, even when operating with just one web server or application server. The reverse proxy acts as the public-facing representation of a website, handling requests from web browsers and mobile apps.
The deployment of a reverse proxy thus serves as a crucial enhancement for web-based systems, offering heightened security, scalability, flexibility, and accelerated performance.
5. Difference between NGINX and Apache
Similarities between NGINX and Apache
Let’s compare the two most popular Web Servers today:
- They are similar in some of the following characteristics:
- All are capable of running on multiple UNIX operating systems.
- There is a mailing system and Stack Overflow forum support.
- There is good security for the source code.
- NGINX connects to PHP using Apache-like concurrency paired with the PHP-FPM Module.
- The two servers have similar performance on dynamic content.
- The running time in the PHP environment of the two servers above is quite similar.
- Both have large user communities
Difference between NGINX và Apache
|
|
NGINX |
Apache |
|
Supported operating systems |
Also runs on some modern Unixes and supports some features for Windows. However, the performance of NGINX on windows is not as strong as Apache. |
Runs on all types of Unix-like systems and fully supports Windows. |
|
User support |
Runs on all types of Unix-like systems and fully supports Windows. |
Lack of user support from the company (Apache Foundation) |
|
Static content |
Can handle up to 1000 connections with static content 2.5 times faster than Apache. Use less memory. |
Handles fewer connections at once and is not as fast as NGINX . |
|
Compatibility |
In 2016, Nginx started supporting Dynamic Modules. |
One advantage is that Apache has been providing Dynamic Modules for a long time. |
6. The Role of NGINX in DevOps
In the realm of software development and operations, NGINX has emerged as a critical component of DevOps practices. Its versatility, efficiency, and adaptability have made it an indispensable tool for managing and delivering web applications. Let’s delve into the multifaceted role of NGINX in the DevOps landscape.
- High-Performance Web Serving
- Load Balancing and Traffic Management
- Reverse Proxying and API Gateways
- Content Caching and Delivery
- Static File Serving and Indexing
- HTTPS Support and SSL Encryption
- Configuration Flexibility and Automation
- Monitoring and Observability
- Scalability and High Availability
- Community Support and Open-Source Ecosystem
In conclusion, NGINX has established itself as an indispensable tool in the DevOps toolkit. Its exceptional performance, versatility, and adaptability make it a critical component for managing and delivering web applications efficiently and securely. As the demand for modern, scalable, and resilient web applications continues to grow, NGINX is poised to play an even more prominent role in the DevOps landscape.
